Revolutions of the Soul
November 12, 2023 Leave a comment
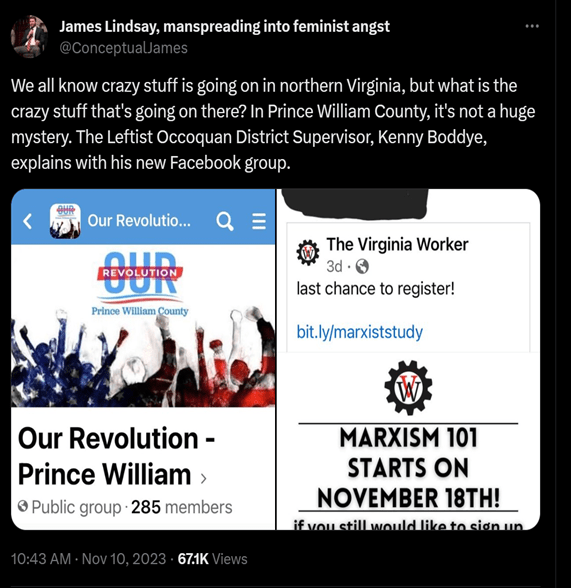
Know this: the issue, whether abortion, gender, sexuality, racism, capitalism, equality, colonialism, Jews or some other oppressor/oppressed power struggle– the issue is never the issue. The revolution is the issue. The key question of any revolution is who holds power, as Lenin wrote.
Many of the revolution’s WOKE reactionaries are blinded by the mythic romance of revolution. Pursuit of revolution itself is seen as something valuable, as taking part in something stylishly ‘Che Guevarean’ and adventurous and something to be passionate about. It may be a religion for some.
The revolution’s WOKE reactionaries are OK with creating suffering and totalitarianism as long as the rhetoric is about total transformation, whatever that entails.
The revolution of the hour: for the destruction of the Western world; we are to be the causalities and they, the martyrs in their romantic myth.
I’ve learned how true revolution takes place. It’s not through mad passions but through everyday empathy and love and the tiny alterations of the heart and mind that move us in that direction . . .
~~~
Literary critic Joseph Epstein, with the title of his book-length essay, asks The Novel, Who Needs It? Turns out, I do, as it offers “truth of an important kind unavailable elsewhere in literature or anywhere else.”
So, I’ve made it a point to read the realist fiction of Russian writers – Solzhenitsyn, Dostoyevsky, Tolstoy, and others along with Chekhov’s short stories.
With a sense of moral urgency, fiction-writing has always been serious business for Russians. The great writers were the truth-tellers, the prophets, the voice of the voiceless, and the conscience of a nation— “a second government,” as Alexander Solzhenitsyn once put it.
Why read great novels and Russian literature today? Gary Saul Morson provides his reasoning:
Like realism in painting, the realism in Russian fiction captures life with an accurate, detailed, unembellished depiction of life. It rejects flowery idealization, fantasy, and supernatural elements, and presents close observation of the human experience which can lead to personal discovery.
Life’s most important questions are explored in Russian fiction. The open-endedness of the writing leaves one to ponder the choices one is making. Literary realism can be grounding.
Ultimately about ideas, superior fiction shows how ideas -ideology and love for two examples – are played out in the lives of the characters. Over time, with tiny alterations, they change their minds –- and you see their conversion. Character development in literary realism is important.
“A single novel can touch on the wildest adventure but also dwell on the most private personal psychology,” writes Epstein. He gives the example of Moby Dick. I went with Tolstoy’s Anna Karenina for the latter.
Anna Karenina (1878), a novel about love and the family, explores the lives of its characters. Some pursue romantic love and others develop mature love. There are heroes and villains in Tolstoy’s most pro-family story.
The consequences of infidelity and the compromises made for forbidden love begin to add up for both Anna and Stiva. In contrast are those well-married and living a rather prosaic life – Kitty and Levin. Over time and with many intimate conversations to understand each other, they have matured from romance to love and found contentment.
Tolstoy at 68 years of age, had just finished Anna Karenina. It has been said by some that as he wrote Anna, Tolstoy was going through a spiritual crisis. He perhaps goes through a very similar spiritual conversion as does Levin.
Tolstoy had been as baptized and raised according to the principles of the Orthodox Christian Church. But later, at eighteen, he said “I no longer believed in anything I had been taught.” I see that as a typical eighteen-year-old response to what feels confining and irrational.
But Tolstoy moves from staunch atheist to a firmly spiritual person. He believed that God was the answer to the type of carnal excess and groundless passions found in the Anna and Vronsky relationship.
Were Levin’s thought processes and his spiritual journey, his tiny alterations of consciousness, also Tolstoy’s spiritual journey? We get a sense of spiritual crisis, of spiritual revolution, and of spiritual maturation in the following four excerpts.
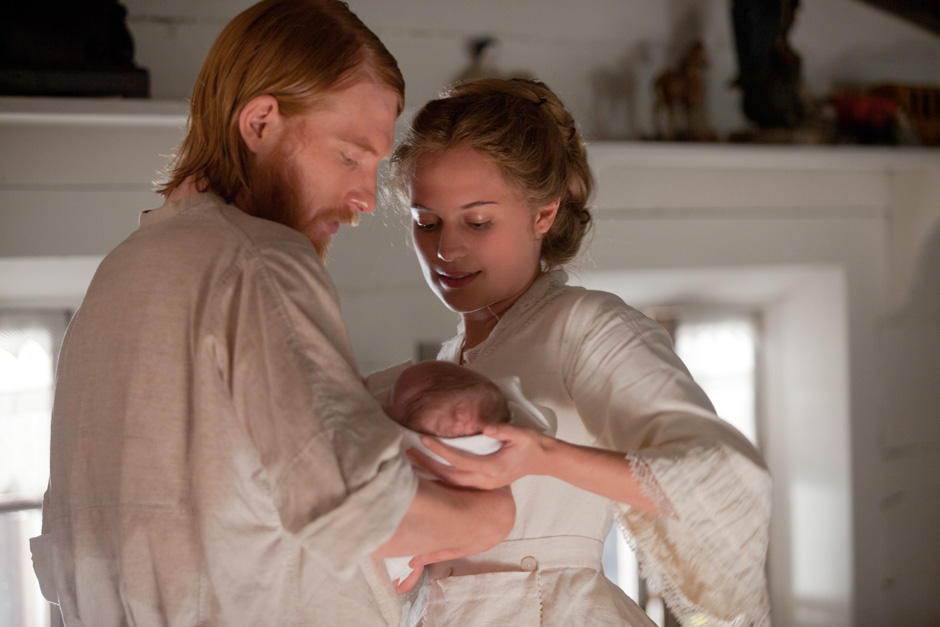
Tolstoy narrates the birth of Levin’s son almost entirely from the new father’s point of view. The birth of his son sparks a spiritual breakthrough in Levin.
Anna Karenina, Part 7, Chapter 13
One night, Kitty awakens Levin with news that her labor has begun. Levin is beside himself, aware only of her suffering and the need to alleviate it. Kitty sends Levin to fetch the midwife and the doctor and to get a prescription from the pharmacist. As he heads for the door, Levin hears a pitiful moan.
“Yes, that’s her,” he told himself, and clutching his head, he ran downstairs.
“Lord have mercy! Forgive us, help us! He repeated the words that suddenly came to his lips out of nowhere, and he, a nonbeliever repeated these words not only with his lips. Now, at this moment, he knew that neither all his doubts nor the impossibility of believing with his reason, which he had known in himself, in any way prevented him from turning to God. Now all that flew from his soul like dust. Who else was he to turn to if not to the One in whose hands he felt himself, his soul, his love?”
Gary Saul Morson, in Anna Karenina in Our Time: Seeing More Wisely,73:
“His reason suspended out of intense empathy, Levin, an unbeliever on rational grounds, finds himself praying, and not “only with his lips” (738). Why he, an atheist, prays sincerely at this moment becomes for him a riddle touching on life’s essential meaning. Desperate to do something but with nothing to do, Levin simply has to endure, a state that (as we shall see with Karenin) provokes the soul torn from its habitual responses to experience the sublime.”
Anna Karenina, Part 7, Chapter 14
Levin is floored, angry that the pharmacist preparing the opium and the doctor drinking his coffee are so laid back – taking their time – about the approach of the birth. He’s in such a state he can’t think straight. For them, the birth was an ordinary event. But for landowner Levin, who had been primarily concerned with farming and agricultural and was writing a theory book about it, there was no place to catalog the event.
Levin has no way to analyze what is happening. “All the usual conditions of life without which it is impossible to form a conception of anything ceased to exist for Levin. He had lost the sense of time.”
When Levin hears Kitty’s first scream, Levin is nonplussed. He has so bonded to Kitty over time that, in empathy, he suffers intense agony. He had experienced the same intense feelings and helplessness as his brother was dying.
“He knew and felt only that what was transpiring was similar to that which had transpired a year before in the provincial town hotel at his brother Nikolai’s deathbed. But that had been grief – and this was joy. Still, both that grief and this joy were identically outside all of life’s ordinary conditions; they were like an opening in that ordinary life through which something sublime appeared. What was transpiring had come about with identical difficulty and agony; and with identical incomprehensibility, the soul, when it did contemplate this sublime something, rose to a height as it had never risen before, where reason could not keep up.
“Lord, forgive and help us,” he repeated to himself incessantly, feeling, in spite of such a long and seemingly total estrangement, that he was addressing God just as trustingly and simply as during his childhood and first youth.”
Anna Karenina, Part 7, Chapter 15
Watching his brother die, Levin thinks that death is a cruel joke – you live, suffer, struggle and suddenly cease to exist. Now seeing his wife in such a painful state and thinking she is dying, he is beside himself: he “had long since given up wanting the child. He now hated the child. He didn’t even wish for her life now, he only wanted a cessation to these horrible sufferings.” New life brings new suffering.
But with the birth of his son and being anchored to life by his new family, Levin then understands that death is merely part of life. He maturely concludes that if one lives “for one’s soul” rather than for illusory self-gratification, the end of life is no longer a cruel trick, but a further revelation of life’s truths.
“If Levin had been told before that Kitty was dead, and that he had died with her, and that their children were angels, and that God was standing before him, he would have been surprised at nothing. But now, coming back to the world of reality, he had to make great mental efforts to take in that she was alive and well, and that the being howling so desperately was his son. Kitty was alive, her suffering was over. And he was inexpressively happy. This he understood and it made him completely happy. But the child? Where had he come from, and why, and who was he? He simply could not understand, could not get used to the idea. It seemed to him something superfluous, something extra, which he could not get used to for a long time.
Anna Karenina, Part 7, Chapter 16
A changed man.
“At ten o’clock the old prince, Sergey Ivanovitch, and Stepan Arkadyevitch were sitting at Levin’s. Having inquired after Kitty, they had dropped into conversation upon other subjects. Levin listened to them and during these conversations could not keep from recalling what had come to pass, what had happened prior to this morning, recalled himself as he had been yesterday, before all this. It was as if a hundred years had passed since then. He felt as if he were on some in accessible height from which he was making an effort to descend in order not to insult the people he was speaking to. He spoke and thought incessantly about his wife, the details of her present condition, and his son, to the idea of whose existence he was trying to accustom himself. The entire feminine world, which had taken on for him a new, previously unknown significance since he had been married, now in his mind had risen so high that his mind could not grasp it. He listened to the conversation about dinner yesterday at the club and thought, “What is happening with her now? Has she fallen asleep? How is she feeling? What is she thinking? Is my son Dimitri crying? And in the middle of the conversation, in the middle of a sentence, he jumped up and left the room.”
. . .
“Her gaze, bright in any case, shone even more brightly the closer he came. On her face was that same alteration from earthly to unearthly that one sees on the face of the dead; but there it is farewell, here a welcome. Again agitation similar to what he had experienced at the moment of the birth overwhelmed his heart. She took his hand and asked him whether he had slept. He couldn’t answer and turned away, convinced of his own weakness.
~~~
These four excerpts offer an opening into the ordinary life of Levin and Kitty. Other characters, the novel’s headliners Anna and Vronsky, go through significant turmoil over their decisions. Dolly, whose husband Stiva was unfaithful, stands out. But not for bad decisions or for the number of mentions, but for her care and love. She simply does what is needed and shows Christian love.
I’ll end with a quote from Gary Saul Morson’s Anna Karenina in Our Time: Seeing More Wisely:, 190:
“In this novel, Christian love produces monstrosity, and real saintliness, if the term can be so used, is inconspicuous. It does not sound a trumpet.
Any doctrine that defies human nature and everyday practices will, if backed by sufficient force, create much greater suffering than it sets out to alleviate. A movement that is truly “revolutionary” – that, like Bolshevism, sets out to change human nature entirely – will create evil on a scale not seen before the twentieth century. Tolstoy saw Christian love, revolutionism, and all other utopian ways of thinking as related errors. If so, they are errors of our time, and perhaps prosaic goodness offers the best hope of correction.”
I would correct the above with “Tolstoy saw insincere Christian love . . .”
~~~~~
The Abiding Truths of Russian Literature – A Conversation with Gary Saul Morson
The Abiding Truths of Russian Literature: A Conversation with Gary Saul Morson – AlbertMohler.com
~~~~~
2017 marks the centenary of the Bolshevik Revolution, an event that tragically reshaped Russian and Western history. How such an extraordinary event, and the ghastly regime it produced, could ever have happened depended not only on a great war, and the theoretical arcana of Karl Marx but, perhaps even more, on the outlook of the Russian intelligentsia and its assumptions about its social role. These same psychological and ideological predispositions continue to be found among intellectuals today. Hence, understanding the cultural setting of the Russian Revolution also helps us understand some of the more dangerous currents in contemporary intellectual life.
“Russian Lessons from 1917” – Gary Saul Morson – YouTube
~~~~~