What’s Your Relationship with Wisdom?
November 27, 2024 Leave a comment
Imagine. You are the half-brother of a new baby brother. The little guy seems to be prized above all else. Certainly, there was a big fuss about his birth. Field workers showed up just to see him. They talked of angels appearing.
A couple years later, sages come from a long way away. They talk of being guided by a star to find a newborn king. They give your half-brother expensive gifts.
Then your father has a dream. He says that authorities want to kill your brother. Your father and step-mother suddenly take your brother and flee to another country. You and your brothers and sisters stay with relatives in Bethlehem. When they return with the boy, your family moves to Nazareth in Galilee. There are too many eyes on Bethlehem, your father says.
You can’t forget the time your family went to up Jerusalem for the Festival of the Passover. Afterward, walking for a day toward home, your step-mother finds out that your half-brother is not around. When asked about his whereabouts, you said “How should I know where he is? Am I his baby sitter?”
Your family walks back to Jerusalem to look for him. Your father and mother ask folks along the way if they’ve seen your brother. It turns out, after three days of looking for that guy, that you find him in the temple courts, sitting among the teachers, listening to them and asking them questions. He’s got their attention! The nerve of your twelve-year kid brother!
Your step-mother was panicky. She was not at all happy when we finally found him. She said to him, “Son, why have you treated us like this? Your father and I have been anxiously searching for you.”
And he says “Why were you searching for me? Didn’t you know I had to be in my Father’s house?” That sounded like crazy talk.
You, Jacob, and your brothers, Joses, Judah, and Simon and your sisters Salome and Mary are astonished at the attention your father and step-mother and others give to your half-brother. You become jealous and find it easy to look askance at him. You are not alone in these feelings.
When he teaches in your synagogue, people whisper “Where’d he get all this? Where’d he get this wisdom? How does he have that kind of power in his hands?” Everyone was wondering “Who is this guy?” “Isn’t he just a local yokel like the rest of us?” They took offense at him.
He is your brother, so you try to reserve judgement. He does say and do astonishing things but you find it really hard to believe in him. He’s been a mystery since the beginning. You and your three brothers think that if he really is such a big deal he should go show himself to the whole world. The four of you push him to do this. But he goes in a deadly direction.
After your half-brother’s resurrection, you are convinced beyond any doubt that he is the Christ, God’s great mystery. You agree with the apostle Paul that he became to us wisdom from God. And, that everything that we have – right thinking and right living, a clean slate and a fresh start – comes from God by way of Jesus Christ.
~~~
Who is Jacob, in translations called James? He was a half-brother of Jesus and therefore, an eyewitness of his life. He was likely one of the sources for the gospel of Luke along with Peter, Cleopas, Mary, and Joanna. James could vouch for the infancy narrative and childhood of Jesus. The gospel of Luke notes, in the account of the boy Jesus at the temple, that “Jesus grew in wisdom and stature, and in favor with God and man.” Both James and Mary would know this.
James is mentioned in the gospel of Mark (6:3) and the gospel of Matthew (13:55). He is in Paul’s list of eyewitnesses who saw the risen Lord (1 Cor. 15: 5-7).
Paul mentions that he received his apostleship in the same tradition as the Jerusalem apostles, including Peter and James (Gal. 1:18). He mentions James first, and then Peter and John, as “pillars” in his allusion to the temple (Gal. 2:9).
After the resurrection, the Jerusalem church became the mother church of the Christian movement under the leadership of The Twelve and James. James is mentioned as head of that church (Acts 12:17; 15:13-21; 21:18-25). (It needs to be said: all first-century Christianity was Jewish. Early Christianity was a distinctive form of Judaism. James writes from the same Jewish heritage and wisdom tradition that Jesus taught from. “Christianity” was not a break from the past.)
Jacob wrote the letter/book of James.
James is considered the Proverbs of the New Testament. Written with knowledge of Jewish wisdom-traditions and Torah, James is simple and direct in his words. He writes wisdom sayings – practical moral instruction. He doesn’t pull any punches.
James instructs us to match faith with good works and to “Show by your good life that your works are done with the gentleness born of wisdom.” And not just any wisdom. We are to choose “wisdom from above” and not the “earthly, unspiritual, devilish” kind. (James 3: 13-18).
It has been suggested that the New Testament book of James “has been heavily influenced by two sources, the first of which is Jesus’ teaching about life in the Kingdom of God, especially the Sermon on the Mount (Matt. 5-7).“ See “hearers and doers” example in Matthew 7: 24-27 and James 1:22-25.
“The second key influence is the biblical wisdom book of Proverbs, especially the poems in Proverbs 1-9.” See Proverbs 1-9 and James 1:5 regarding the importance of acquiring wisdom.
Reading James, I see the parallels and influence of Proverbs and the Sermon on the Mount. I also read James in terms of another selection of wisdom literature: the Book of Job. Therein, hardships and trials require a new perspective. The letter of James, written to the Jewish Christians throughout the Diaspora, speaks of the need for wisdom and Job-like perseverance in a world where people struggle and suffer because of what they profess.
Read James with the Book of Job in mind:
My brothers and sisters, whenever you face various trials, consider it all joy, because you know that the testing of your faith produces endurance. And let endurance complete its work, so that you may be complete and whole, lacking in nothing.
And . . .
Blessed is anyone who endures temptation. Such a one has stood the test and will receive the crown of life that the Lord has promised to those who love him. No one, when tempted, should say, “I am being tempted by God,” for God cannot be tempted by evil and he himself tempts no one. But one is tempted by one’s own desire, being lured and enticed by it; then, when desire has conceived, it engenders sin, and sin, when it is fully grown, gives birth to death. (James. 1: 12-15)
And . . .
Indeed, we call blessed those who showed endurance. You have heard of the endurance of Job, and you have seen the outcome that the Lord brought about, for the Lord is compassionate and merciful. (James. 5:11)
The Book of Job tell us where not to look for wisdom. Job 28: 12-15 says that we won’t find wisdom and understanding in the human realm:
“But where shall wisdom be found?
And where is the place of understanding?
Mortals do not know the way to it,
and it is not found in the land of the living.
The deep says, ‘It is not in me,’
and the sea says, ‘It is not with me.’
It cannot be gotten for gold,
and silver cannot be weighed out as its price.”
James tells us where to look for wisdom:
If any of you is lacking in wisdom, ask God, who gives to all generously and ungrudgingly, and it will be given you. But ask in faith, never doubting, for the one who doubts is like a wave of the sea, driven and tossed by the wind. For the doubter, being double-minded and unstable in every way, must not expect to receive anything from the Lord. (James. 1: 5-8)
~~~
The Lord by wisdom founded the earth;
by understanding he established the heavens;
by his knowledge the deeps broke open,
and the clouds drop down the dew.
Prov. 3: 19-20
The Lord created me [Lady Wisdom] at the beginning of his work,
the first of his acts of long ago.
Ages ago I was set up,
at the first, before the beginning of the earth. . .
I was beside him, like a master worker,
and I was daily his delight,
playing before him always,
playing in his inhabited world
and delighting in the human race.
Prov. 8: 22,30-31; Proverbs 1:20–33 and Proverbs 8:1—9:12
Christians typically start their version of the creation narrative in Genesis 1 and 2. I start with what many scholars consider, based on archaic language, style, themes, and similar works, the oldest book of the Bible, the Book of Job. After hearing the human perspective about the cosmos from Job’s friends, I want the Divine perspective which includes the Wisdom Hymn in Job 28.
God alone knows the way to Wisdom,
he knows the exact place to find it.
He knows where everything is on earth,
he sees everything under heaven.
Job and his friends thought the world worked a certain way. They thought God acted a certain way. But they lacked Divine perspective – wisdom. After all that is said in the human realm, God questions Job from out of a whirlwind:
“Where were you when I laid the foundation of the earth? Tell me, if you have understanding.”
“Have you ever in your days commanded the morning light?”
“Where does light live, or where does darkness reside?”
“Can you lead out a constellation in its season?”
God reveals to Job and his friends their utter lack of understanding of how the complex cosmos is ordered. He describes intricate wonders of creation (Job 38-41) and challenges Job to even begin to understand His world. It becomes quickly evident that it is not their place to question God’s rectitude or wisdom.
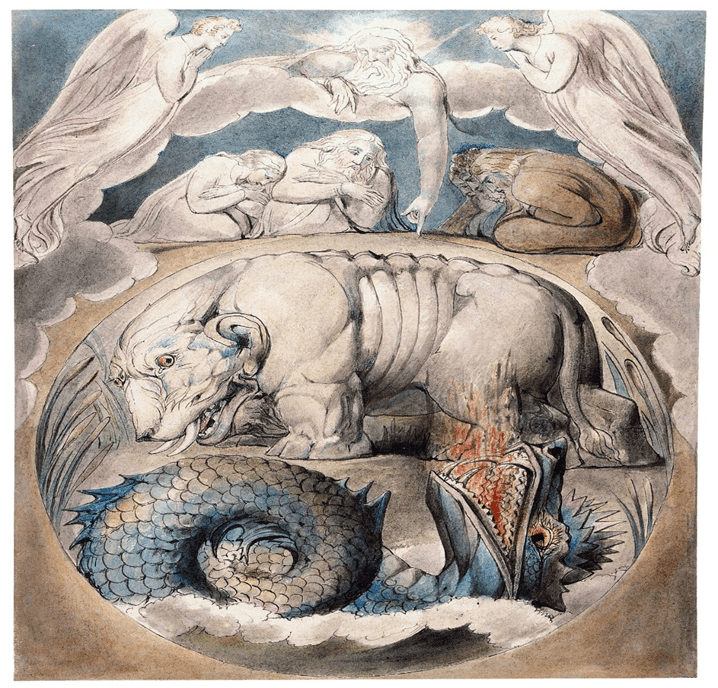
To illustrate further, God instructs Job with the ways of Behemoth and Leviathan (Job 40-41).
Wisdom from God matches us up with the created order and the Creator. Wisdom is working with God’s created order, avoiding disorder and recognizing non-order (John Walton). See Uncharted Understanding | Kingdom Venturers
Having information is not having knowledge. Having information is not having wisdom. Knowledge is knowing what to do with information. Wisdom is understanding, discernment, and character supplied by God and applied with knowledge. Lady Wisdom calls us to good sense, sound judgment, and moral understanding. Wisdom has the capacity to contemplate profounder problems of human life and destiny.
It is the wisdom of the clever to understand where they go,
but the folly of fools misleads. Prov. 14:8
To get wisdom is to love oneself;
to keep understanding is to prosper. Prov. 19:8
Buy truth, and do not sell it;
buy wisdom, instruction, and understanding. Prov. 23:23
James, steeped in Jewish wisdom-traditions, knows that wisdom belongs to the very nature of God himself. He knows that wisdom comes to man only as a divine gift. He writes telling readers to ask for the divine gift of wisdom by faith.
If you don’t know what you’re doing, pray to the Father. He loves to help. You’ll get his help, and won’t be condescended to when you ask for it. Ask boldly, believingly, without a second thought. People who “worry their prayers” are like wind-whipped waves. Don’t think you’re going to get anything from the Master that way, adrift at sea, keeping all your options open. (James 1:5-8)
The beast Behemoth is not worried:
A raging river does not alarm it;
it is secure, though the Jordan should surge against its mouth.
-Job 40: 23
~~~~~
Proverbs: Lady Wisdom and Lady Folly
Proverbs: Lady Wisdom & Lady Folly
~~~~~
Foster Care
Ronda Paulson and her husband Corey founded Isaiah 117 House to provide a safe and loving home for children awaiting placement in the foster care system. Isaiah 177 House was featured on Mike’s Facebook show, Returning the Favor. Ronda tells how her appearance on the show affected her mission, her life, and especially her health.
~~~~~
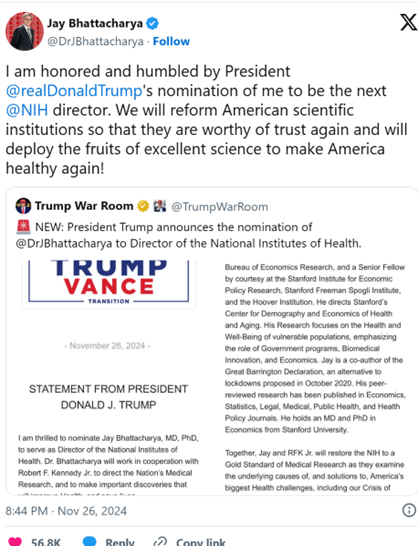
https://x.com/i/status/1861189891985678696
Wisdom (and the restoration of Democracy):
The Trump-Vance transition team announced that Stanford Professor Jay Bhattacharya, MD, PhD, author of “The Great Barrington Declaration,” is his pick to lead the National Institutes of Health. This is a terrific choice; Dr. Bhattacharya is highly respected and was right about the negative effects of lockdowns during the COVID pandemic when so many others were wrong. He didn’t back down despite numerous attempts to silence him. (Emphasis mine.)
(Professor Jay Bhattacharya is ten-thousand times better than former NIH director Dr. Francis Collins!!)
What Jay Bhattacharya, Trump’s NIH Pick, Has Said About Anthony Fauci – Newsweek
Restoring order (and Democracy):
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum addressed U.S. President-elect Donald Trump’s renewed threats of steep tariffs this week, asserting that migrant caravans are no longer reaching the U.S.-Mexico border.
Migrant Caravans Not Reaching Border, Claudia Sheinbaum Says After Trump Threats – Newsweek
~~~